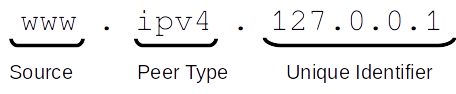24 KiB
Executable file
Internet Federation Database Standard (IFDS) Version 1
IFDS (Internet Federation Database Standard) is a standard database system to which allows internet clients both authorized and public users to query the database to check if the given content or entities involved in the communication could be classified as spam or malicious, allowing a client to take place protections against spam and malicious content on various communication channels such as email, social media, messaging apps, and more.
Introduction
Table of Contents
- Internet Federation Database Standard (IFDS) Version 1
- Introduction
- Table of Contents
- Definitions
- Clients
- Federation Standard
- Query Document
- Platforms
Definitions
Some definitions used in this document, these definitions are not official and are only used to provide a better understanding of the document and the purposes behind features and fields.
-
Peer - Everything from users, bots, channels, groups, and more is considered a peer, a peer is represented by a standard federated address, see Standard Federated Addresses for more information, a peer could be a parent or child of another peer, for example, a user could be a child of a group or channel with an association type of "member", a peer could also be a parent of another peer, for example, a group or channel could be a parent of a user with an association type of "owner" or "admin", these associations are only made known by trusted clients if specified in the QueryDocument, see QueryDocument for more information.
-
Discovery - The process of using the provided information in a QueryDocument to discover & collect information about the content or entities involved in the communication, allowing the database to keep a record of or to have a better understanding of peer associations, content, and more. Discovery is not required for a QueryDocument to be valid, however, it is recommended to provide as much information as possible to allow the database to have a better understanding of the content or entities involved in the communication.
Clients
TODO: Write this section
Client TOTP Signature
TODO: Write this section
Client Object
TODO: Write this section
Federation Standard
The federation standard is a standard which defines how clients should communicate with servers, the standard
Available Types
ClientIdentity Object
The ClientIdentity object is used to identify the client, this standard object contains information about what client is invoking the method, this object is required to be provided by all clients when invoking a method, this object is used by the server to determine if the client is authorized to invoke the method and to determine what permissions the client has.
In such cases where a peer is attempting to invoke a method through a client such as, the server will identify the
invoker as the peer on behalf of the client, this is done by providing the peer's standard federated address in the
peer field of the ClientIdentity object
| Parameter | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
client_uuid |
string |
Yes | The UUID of the client that is invoking the request |
client_totp_signature |
string |
No | Optional. The client's TOTP signature that proves the request came from the client, only applicable if the client uses authorization |
peer |
string |
No | Optional. The peer that's invoking the command on behalf of the client |
Note: If a server has strict permissions enabled, in such cases where the peer has higher permissions than the client, the server will default to maximum permissions as the client rather than the peer, this is to prevent clients without high permissions from abusing the system by using a peer with higher permissions.
Invokable Methods
Invokable Methods are used by clients, peers or the server to invoke a method on the server, the server will use the provided information to determine who's invoking the method and if the method is allowed to be invoked by the peer.
All these methods are standard and required to be implemented by all servers, however, approach would allow for servers to implement additional methods to allow for additional functionality that may not be available in the standard, however, this would require the client to be aware of the additional methods and the server to be aware of the additional methods.
These methods are supposed to invokable by a virtual shell or API endpoint, however, this means while the client does not need to implement or use the shell to invoke these methods but can use the API to achieve the same result as the shell.
ping Method
The ping method is used to check if the server is online and to check the server's version, the ping method is available to all peers. Returns True if the execution was successful, otherwise the client should assume the server is offline or the server is temporarily unreachable.
JSON-RPC Example:
> {"jsonrpc": "2.0", "method": "ping", "id": 1}
< {"jsonrpc": "2.0", "result": true, "id": 1}
Shell Example:
$ ping
true
Default Permission Table:
| root | admin | operator | agent | client | guest |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
whoami Method
The whoami method is used to check the client's permissions and other information, the whoami method is available
to all peers. Returns the identified "uid" of whoever is invoking the method, this can either be root if the
function is being invoked by the server or from the root shell, or the client's UID if the function is being invoked
by a client or finally the peer's Standard Federated Address if the function is being invoked by a peer.
JSON-RPC Example:
> {"jsonrpc": "2.0", "method": "whoami", "id": 1}
< {"jsonrpc": "2.0", "result": "root", "id": 1}
Shell Example:
$ whoami
root
Default Permission Table:
| root | admin | operator | agent | client | guest |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
create_client Method
The create_client method is used to create a new client, the create_client method is only available to the root & admin user by default, however, this can be changed by the server's configuration. Returns the UID of the newly created client if the execution was successful
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
uid |
string |
Yes | The user ID of that is invoking the method |
totp_signature |
string |
Yes | The TOTP signature for authentication |
name |
string |
Yes | The username of the client |
Standard Federated Addresses
A standard federated address is a universally unique identifier which can represent multiple types of peers from different platforms, federated address formats are standardized so only one format is required to be used by clients and allows servers to reject requests to platforms that are not supported by the server.
The format of a standard federated address is as follows:
source.type:id
source- The platform/source where the peer is from, must be a supported platform, see Platformtype- The type of peer, peer types are unique to the platform, see the platform's documentation for more informationid- The unique identifier of the peer, the identifier must be unique to the platform, see the platform's documentation for more information
Even though the value types are defined by the platform's specifications for the federated address, the end result will always be a parsable address that can be used by the server to identify the peer.
When coming up with a federated address standard for a platform, it is important to keep in mind that id must be
unique to the peer on the platform, for example, if a platform has a username system it is best to avoid using something
that can be changed by the user such as a username, instead, use something that is unique to the peer such as an ID or
UUID provided by the platform, this will ensure that the federated address will always be valid and will always point
to the correct peer even if the peer changes their username or other information that isn't unique to the peer.
For a regex pattern to match a standard federated address, see the following:
(?<source>[a-z0-9]+)\.(?<type>[a-z0-9]+):(?<id>.+)
Query Document
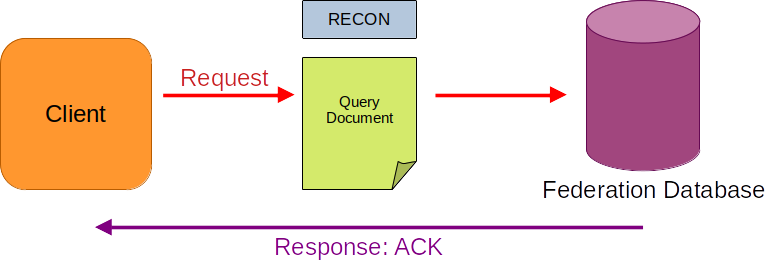
QueryDocument is a query document constructed by the client which presents the contents of the message or event to either be put into discovery, analyzed for spam or malicious content, or report an event where a report has been produced either by a client's automated system or by manually by a user.
QueryDocument Versioning
The version of the QueryDocument is represented by the version field, the version must always be "1" for now, future
versions of the QueryDocument structure may be introduced in the future, to ensure backwards compatibility, the
version field must be checked to ensure the server can parse the document correctly. If the server does not support
the version of the document, the server must reject the document and return an error to the client.
QueryDocument Subject Types
The subject type of the QueryDocument is represented by the subject_type field, the subject type must be one of the
following values:
TODO: Write this section
RECON
TODO: Write this section
ANALYZE
TODO: Write this section
REPORT
TODO: Write this section
QueryDocument Event Types
The event type of the QueryDocument is represented by the event_type field, the event type must be one of the
following values:
- GENERAL - The event is a general event that does not fit into any other event type, the
GENERALevent type is used for events such as a general update to a peer's activity or status that could be used to keep the database up to date with the peer's activity or status. - INCOMING - The event is an incoming message/request from a peer, the
INCOMINGevent type is used for events such as a message/request from a peer that was captured by the client. - OUTGOING - The event is an outgoing message/request to a peer, the
OUTGOINGevent type is used for events such as a message/request to a peer that was captured by the client. - PEER_JOIN - The event is a peer join event, the
PEER_JOINevent type is used for events such when a peer joins or connects to thechannel_peer - PEER_LEAVE - The event is a peer leave event, the
PEER_LEAVEevent type is used for events such when a peer leaves or disconnects from thechannel_peer - PEER_BAN - The event is a peer ban event, the
PEER_BANevent type is used for events such when a peer is banned from thechannel_peer, in such cases thefrom_peeris the peer that banned theto_peerand theto_peeris the peer that was banned. - PEER_UNBAN - The event is a peer unban event, the
PEER_UNBANevent type is used for events such when a peer is unbanned from thechannel_peer, in such cases thefrom_peeris the peer that unbanned theto_peerand theto_peeris the peer that was unbanned. - PEER_KICK - The event is a peer kick event, the
PEER_KICKevent type is used for events such when a peer is kicked from thechannel_peer, in such cases thefrom_peeris the peer that kicked theto_peerand theto_peeris the peer that was kicked. - PEER_RESTRICT - The event is a peer restrict event, the
PEER_RESTRICTevent type is used for events such when a peer is restricted from thechannel_peer, in such cases thefrom_peeris the peer that restricted theto_peerand theto_peeris the peer that was restricted. - ANNOUNCEMENT - The event is an announcement event, the
ANNOUNCEMENTevent type is used for events such as an announcement from thechannel_peerthat was captured by the client, optionally, thefrom_peerfield can be used to specify the peer that made the announcement, if thefrom_peerfield is not specified, the announcement is assumed to be from the `channel_peer
Events are used to give the database context about what's happening in the channel, for example, a server with anomaly detection may use the events to determine if a peer is sending too many messages in a short period of time or a channel is being raided by a group of peers.
In all other cases GENERAL may be used if the client is simply doing RECON requests to keep the database up to date
with the peer's activity or status.
QueryDocument Object
The QueryDocument is a JSON object which contains the following fields:
| Name | Type | Required | Example Value(s) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
version |
string |
Yes | 1 |
The version of the QueryDocument, must always be "1" |
subject_type |
string |
Yes | RECON, ANALYZE or REPORT |
The subject type, must be "RECON", "ANALYZE" or "REPORT" |
client_id |
string |
Yes | 00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000 |
The client's unique UUIDv4 identifier to identify who the document is from |
client_totp_signature |
string |
No | a94a8fe5ccb19ba61c4c0873d391e987982fbbd3 |
The client's TOTP signature to verify the client's identity with the document's reported timestamp, if the client does not use authentication, this field is not required, see Client TOTP Signature |
timestamp |
int |
No | 1614556800 |
The timestamp of the document, if the client does not use authentication, this field is not required instead the server will use the server's timestamp. |
platform |
string |
Yes | telegram.org, email, discord.com, etc. |
The platform of the message or event, must be a supported service, see Platform |
event_type |
string |
Yes | incoming_message, peer_join, peer_leave, etc. |
The event type of the message or event that is represented by the document, this provides the server with context to detect anomalies in the document, see Event Type |
channel_peer |
string |
No | telegram.chat:-1001301191379 |
The channel peer represented as a Standard Federated Address in which the content was sent in, this could be a communication channel or chat room where one or more peers may use to broadcast messages on, see Standard Federated Addresses |
resent_from_peer |
string |
No | telegram.user:123456789 |
The resent from peer represented as a Standard Federated Address in which the content was resent/forwarded from, this could be a peer who has resent the content from another peer, see Standard Federated Addresses |
from_peer |
string |
No | telegram.user:123456789 |
The from peer represented as a Standard Federated Address in which the content was sent from, this could be a peer who has sent the content, see Standard Federated Addresses |
to_peer |
string |
No | telegram.user:123456789 |
The to peer represented as a Standard Federated Address in which the content was sent to, this could be the intended recipient of the content, see Standard Federated Addresses |
proxy_peer |
string |
No | telegram.user:123456789 |
The proxy peer represented as a Standard Federated Address in which the content was sent through a proxy, if identified as a proxy that could be mean from_peer is not the original sender of the content but instead the proxy peer is, see Standard Federated Addresses |
peers |
Peer[] |
No | N/A | The peer definitions of the document, see Peer |
content |
Content |
No | N/A | The content of the document if applicable to the event type, see Content |
attachments |
Attachment[] |
No | N/A | Optional attachments if the content contains any, see Attachment |
reports |
Report[] |
No | N/A | Optional reports if the content contains any, see Report |
Note
: The
timestampfield is not required if the client uses authentication, instead the server will use the server's timestamp to verify the document's timestamp, if the client does not use authentication, thetimestampfield is required to verify the document's timestamp.
Note
:
peersuses the Standard Federated Address as the key
Note
:
attachmentsuses the File Name as the key
QueryDocument.Peer Object
TODO: Write this section
QueryDocument.Content Object
TODO: Write this section
QueryDocument.Attachment Object
TODO: Write this section
QueryDocument.Report Object
TODO: Write this section
Platforms
TODO: Write this section
Telegram
TODO: Write this section